There's something truly special about enjoying fresh, ripe strawberries, picked right from your own garden. That burst of sweetness, the vibrant red color—it's a reward that makes all the effort worthwhile. For many who dream of this delightful experience, a common question often pops up: how long do strawberries take to grow? It's a very practical thought, especially when you're eager to taste those homegrown berries.
You might be wondering about the timeline, about when you can actually expect to see those little green fruits turn into juicy red treasures. Well, the answer isn't always a single number, as it truly depends on a few things. Knowing the typical growth phases and what helps them along can make all the difference, so you can plan your garden with a good idea of when harvest time might arrive.
Growing strawberries can be a really rewarding project, and it's actually quite accessible for most home gardeners. Whether you're starting with tiny seeds or established plants, understanding the journey from a small beginning to a fruit-laden plant is key. Let's explore the various ways strawberries grow and what you can do to support their progress, so you're ready for that delicious first bite.
Table of Contents
- The Strawberry Growth Journey: How Long Do Strawberries Take to Grow?
- Understanding the Strawberry Life Cycle
- Factors Influencing Strawberry Growth Time
- Caring for Your Strawberries for a Timely Harvest
- Strawberries as Perennial Plants
- Frequently Asked Questions About Strawberry Growth
The Strawberry Growth Journey: How Long Do Strawberries Take to Grow?
When you set out to grow strawberries, the time it takes to see those sweet fruits can vary quite a bit, depending on how you start your plants. It's actually a really interesting process, and knowing the different timelines helps manage your expectations. So, let's look at the common ways people begin their strawberry patches and what kind of wait you can expect for each method.
From Seed to Fruit: A Patient Path
Starting strawberries from seed is, in a way, the longest route to a harvest, but it can be quite satisfying. My experience has shown that it takes a plant 60 to 90 days to mature from a seed into a tasty fruit. This period covers the entire development, from a tiny sprout to a plant ready to give you berries. It's a bit of a marathon, if you will, compared to other starting methods.
If you're wondering about the very first signs of life, from seed, strawberries will take around 110 days from sprouting until they start to flower. This means you're looking at a few months before you even see those delicate white blossoms that promise future fruit. Christopher, a seasoned gardener, often points out that if you're growing yours from seed, patience is very much a key ingredient. It's a commitment, but the reward of growing from scratch is pretty big.
This longer timeline for seeds is mostly because the plant needs to establish a strong root system and sufficient foliage before it can put energy into producing fruit. It's almost like a child growing up; they need time to develop before they can take on bigger tasks. So, if you choose the seed path, prepare for a bit of a wait, but know that it's a very natural process.
Quicker Starts: Plugs, Runners, and Bare Roots
For those who are a little less patient or just want a head start, most people prefer to grow strawberries from plug plants, runners, and bare root plants. These methods generally cut down the waiting time significantly. It's like getting a plant that's already been through its early schooling, ready to move on to the next phase.
If you choose bare root plants, depending on the variety, strawberries take 60 to 90 days to mature from planting until they are ready to pick. This is a much faster turnaround compared to seeds, as the plant already has an established structure. It's a popular choice for many home growers because it offers a relatively quick path to fruit.
Strawberry transplants, whether they are plugs or runners, typically take around 90 days, which is about three months, to produce fruits. So, if you get these established plants in the early spring, you could be enjoying fresh berries by early summer. It's a pretty efficient way to get your strawberry patch going, and many gardeners find this method very satisfying for its speed.
If you plant strawberries in the early spring, they will take about 60 days to grow from transplanting to ripe fruit. However, if you wait until late spring or summer to plant, the timeline might shift a bit, as the plants will be influenced by the changing light and temperature conditions. This is why timing your planting in the spring can be rather beneficial for a quicker harvest.
Understanding the Strawberry Life Cycle
Strawberries are fascinating plants, and they go through distinct phases of growth on an annual cycle. This cycle repeats each year, which is why they are considered perennial plants, meaning they can live and produce fruit for several years. Knowing these stages helps you care for them better and anticipate when your berries will appear.
Four Key Stages of Growth
The growth cycle of strawberries can be divided into four key stages. These phases basically guide the plant from its very beginning to producing those lovely fruits. It's a predictable pattern that the plant follows each year, ensuring a steady supply of berries if cared for properly.
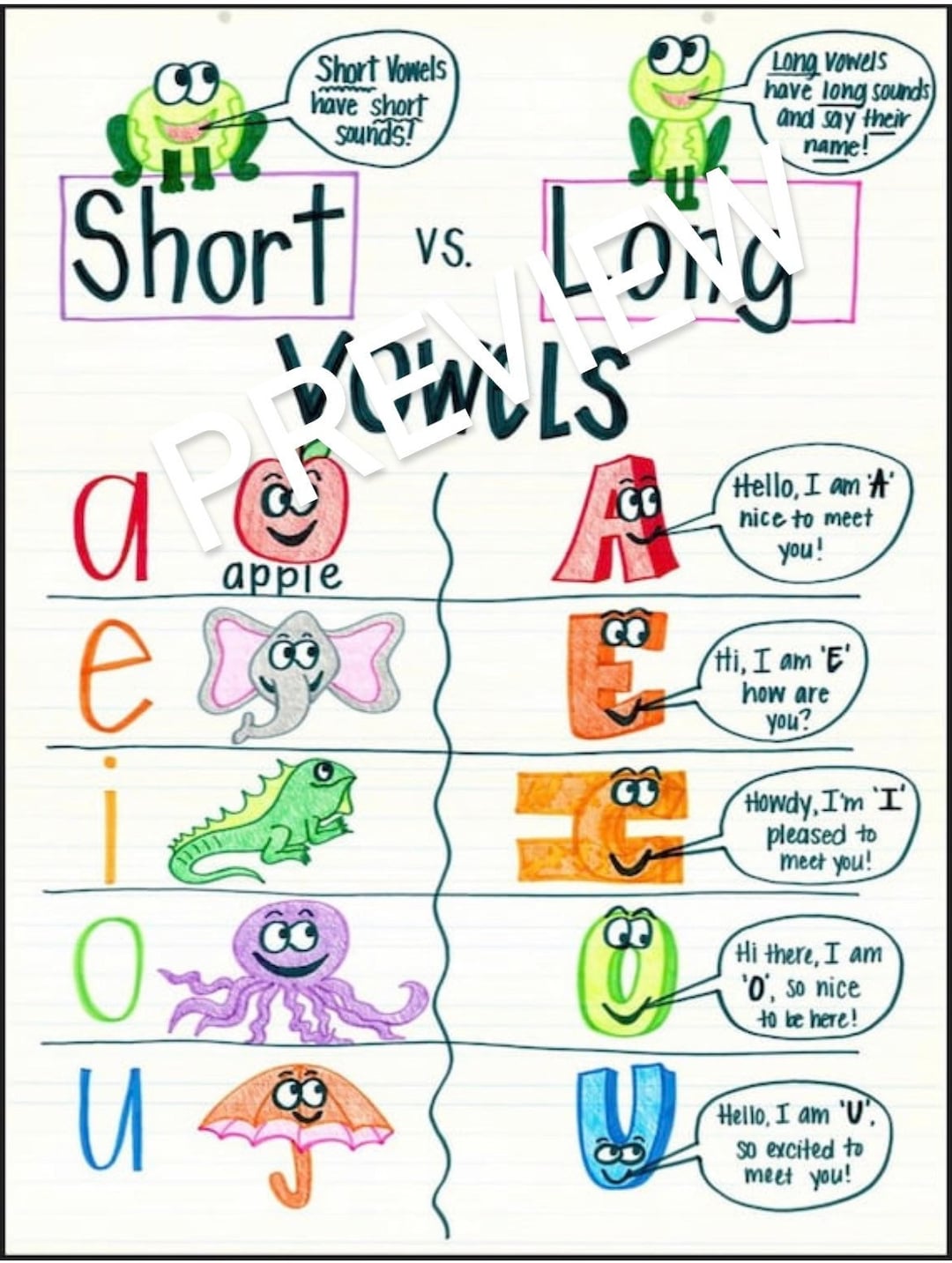
The first stage is **Germination**. This is the initial stage where the seed sprouts and begins to form a tiny plant. For seeds, this is where the long journey truly begins, establishing the very foundation of the plant. It's a delicate phase, and consistent moisture is pretty important here.
Next comes **Vegetative Growth**. During this phase, the plant focuses on developing its leaves, roots, and runners. This is where the plant gets bigger and stronger, gathering the energy it will need for fruiting. Strong vegetative growth is actually quite crucial for a good harvest later on, as it builds the plant's capacity.
Following that is **Flowering and Fruiting**. This is arguably the most exciting stage for gardeners! The plant produces flowers, which then get pollinated and develop into berries. This is when you start to see the promise of your hard work. The little green nubs begin to swell and change color, which is a very welcome sight.
Finally, there's **Maturity**. This stage involves the full ripening of the fruits, making them ready for picking. After fruiting, the plant might produce more runners, which are basically baby plants that can be used to expand your patch. The plant then prepares for a dormant period, only to repeat the cycle again next year, which is rather amazing.
From Flower to Fruit: The Ripening Period
Once your strawberry plants start to flower, you're on the home stretch to enjoying fresh berries. On average, it takes 4 to 6 weeks from flower bud initiation to the onset of fruiting. However, some varieties may take longer, up to 12 weeks, to produce mature fruits. So, the type of strawberry you chose can really influence this final stretch.
The average strawberry ripening time, from the very start of the plant's growth to harvest, is three months. This period includes the whole growing process up to harvest time. For example, in the 7a US growing zone, the average strawberry season typically runs from March to June. This means if you get your plants in early spring, you can expect berries by early summer.
As the weather begins to warm up in spring, your plants will put out leaves, and then those lovely flowers will appear. From those flowers, the berries will form and begin to swell. Watching them turn from small, hard green nubs to plump, red, juicy fruits is a pretty satisfying part of the gardening experience. It's a quick transformation once the flowers have been pollinated, which is kind of neat to observe.
Factors Influencing Strawberry Growth Time
While we can give general timelines for how long do strawberries take to grow, several environmental conditions and choices you make can actually speed up or slow down the process. It's not just about planting and waiting; providing the right environment makes a real difference. So, let's explore what helps these plants thrive and produce fruit more quickly.
Sunshine is Key
One of the most important things for strawberry plants is sunlight. Strawberry plants require 6 to 10 hours of direct sunlight a day, so choosing a sunny spot for your patch is absolutely crucial. Without enough sun, the plants might grow, but they won't produce as many flowers or as much fruit, and the fruit they do produce might not be as sweet or ripen as quickly. It's basically their fuel for growth and fruit production, so more sun usually means better results.
A spot that gets full sun for most of the day is really ideal. If they are in too much shade, you'll find that their growth is a bit stunted, and the berries might stay small or never fully develop their rich color and flavor. So, before you even plant, take some time to observe your garden and pick the sunniest spot you have available. This one step can make a very big impact on your harvest.
Soil Matters, But Not Too Much
When it comes to soil, strawberries are actually quite tolerant of different soil types. This is good news for many gardeners, as it means you don't need extremely specific soil conditions. However, they do prefer loamy soil that drains well. Loamy soil is a mix of sand, silt, and clay, offering a good balance of moisture retention and drainage. It's kind of the perfect middle ground for many plants.
If your soil is too heavy with clay, it might hold too much water, which can lead to root problems. If it's too sandy, it might drain too quickly, meaning the plants don't get enough moisture. So, while they are tolerant, aiming for that well-draining loamy soil will certainly help your plants grow better and produce more fruit. The growth rate, you see, depends on the variety and factors such as soil conditions, so getting the soil right is pretty important.
Variety Choices Affect Timing
The specific variety of strawberry you choose will also play a role in how long it takes for them to grow and produce. Some varieties are known for being early producers, while others might take a bit longer. For example, depending on the variety, strawberries can take 60 to 90 days to mature from bare root. This means some types will give you berries faster than others.
Learning how to grow strawberries from seedlings to fruit in three months, and how to extend your growing season with different varieties, is a great tip. Everbearing varieties, for instance, might produce berries throughout the summer, while June-bearing varieties will give you one big harvest in early summer. Choosing the right variety for your climate and your desired harvest schedule can really optimize your growing experience. It's basically about picking the right tool for the job.
Your Growing Conditions Make a Difference
Ultimately, the growing circumstances you establish will determine how long the process takes. This includes everything from the amount of water they receive to the nutrients in the soil, and even the temperature. The duration of the developing phase depends on the growing conditions you create. Providing consistent care and ideal conditions helps the plants grow steadily and produce fruit efficiently.
This means paying attention to details like watering regularly, especially during dry spells, and making sure they have enough nutrients. It's a bit like nurturing anything; the more consistent and appropriate the care, the better the outcome. A happy strawberry plant, with all its needs met, will typically grow faster and yield more fruit, which is rather simple to understand.
Caring for Your Strawberries for a Timely Harvest
To ensure your strawberries grow well and produce fruit within the expected timeframe, good care is actually quite important. It's not just about planting them and hoping for the best; a little bit of ongoing attention can make a huge difference in your harvest. So, let's talk about some practical tips for keeping your strawberry plants happy and productive.
Preparing the Ground
Before you even put your plants in the ground, preparing the soil properly sets them up for success. You can find tips on soil preparation, fertilizer, pollination, and more, which are all part of getting things ready. This means making sure your soil is well-draining and has the right nutrients. If your soil isn't naturally loamy, you might want to add some compost or other organic matter to improve its structure and fertility.
Good soil preparation basically gives your strawberry plants a strong foundation to grow from. It's like building a house; a solid foundation makes everything else much easier and more stable. Taking this step at the beginning can prevent a lot of problems down the road and help your plants thrive. It's a very simple step that yields big results.
Nourishing Your Plants
Once your strawberries are planted, providing them with the right nutrients is pretty vital. This often involves using a balanced fertilizer. The plants need various elements to support their leaf growth, flower production, and fruit development. Just like we need a good diet, plants need the right mix of nutrients to perform their best.
Too much of one nutrient or too little of another can actually hinder growth. So, following fertilizer instructions and applying it at the right times, often when the plants are actively growing or before flowering, can really boost your yield. It's a way of giving them an extra push to grow strong and produce plenty of delicious berries.
Pollination's Role
For strawberries to produce fruit, their flowers need to be pollinated. This is a very natural process, often carried out by bees and other insects. If you're growing strawberries outdoors, nature usually takes care of this for you. However, if you're growing them indoors or in a protected environment, you might need to help with pollination, perhaps by gently shaking the plants or using a small brush to transfer pollen between flowers.
Good pollination means more flowers turn into fruit, and the fruits are often larger and better formed. It's a simple, yet absolutely crucial step in the fruit-making process. Without effective pollination, you might see plenty of flowers but very few actual berries, which is a bit of a disappointment.
Extending the Season
You can learn how to grow strawberries from seedlings to fruit in three months, and how to extend your growing season with different varieties. For instance, planting a mix of June-bearing and everbearing varieties can give you berries over a longer period. June-bearing types offer a concentrated harvest in early summer, while everbearing types produce smaller flushes of berries throughout the warmer months. This strategy allows you to enjoy fresh strawberries for a much longer time.
Also, using techniques like row covers or growing in containers that can be moved can help protect plants from early frosts or extend their growing period into cooler weather. These methods basically stretch out the time you have for harvesting, giving you more opportunities to enjoy your homegrown fruit. It's a clever way to maximize your efforts and get the most out of your strawberry patch.
Strawberries as Perennial Plants
One really great thing about strawberries is that they are perennial plants. This means they can live and produce fruit for several years, which is quite convenient for gardeners. You don't have to replant them from scratch every single year, which saves a lot of effort and time. This characteristic makes them a very popular choice for home gardens.
They go through distinct phases of growth on an annual cycle. This cycle repeats each year, as the plants emerge from dormancy in the spring, grow, flower, fruit, and then prepare for winter again. Understanding this annual rhythm