Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Privileged Access Management (PAM): A Core Cybersecurity Pillar
- The Core Components and Strategies of PAM
- PAM in Action: Safeguarding Sensitive Data and Systems
- Implementing PAM: Best Practices for Organizations
- The E-E-A-T and YMYL Principles in PAM
- The Future of Privileged Access Management
- Conclusion
In an increasingly interconnected digital world, the security of an organization's most valuable assets hinges on its ability to control and monitor access to critical systems and sensitive data. This is where Privileged Access Management (PAM) emerges as an indispensable cybersecurity solution, acting as a digital gatekeeper that ensures only authorized individuals and processes can interact with an organization's crown jewels. As cyberthreats grow in sophistication and frequency, understanding and implementing robust PAM strategies is no longer optional but a fundamental requirement for business continuity and data integrity.
The concept of "privileged access" extends beyond just IT administrators; it encompasses any human or non-human account with elevated permissions that can significantly impact an organization's operations or data. From database administrators and network engineers to automated scripts and applications, these privileged identities represent the keys to the kingdom. Without proper management, they become prime targets for malicious actors, making Privileged Access Management a cornerstone of a resilient cybersecurity posture.
Understanding Privileged Access Management (PAM): A Core Cybersecurity Pillar
What is PAM?
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is an identity security solution that helps protect organizations against cyberthreats by monitoring, detecting, and preventing unauthorized access. It is a type of identity management and a crucial branch of cybersecurity that focuses on the control, monitoring, and protection of privileged accounts. PAM consists of the cybersecurity strategies and technologies for exerting control over the elevated (“privileged”) access and permissions for identities, ensuring that access to an organization’s most sensitive data and critical systems is meticulously controlled and safeguarded.
At its core, PAM identifies the people, processes, and technology that need privileged access and specifies policies to secure sensitive resources in an organization. It's not just about blocking access; it's about granting the right level of access to the right entity, for the right amount of time, and for the right purpose, all while maintaining a comprehensive audit trail.
Why is PAM Crucial in Today's Threat Landscape?
The digital landscape is fraught with risks. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and insider threats are daily occurrences, often exploiting weaknesses in access control. Privileged accounts, by their very nature, offer attackers the quickest path to an organization's most valuable assets. If a cybercriminal gains control of a privileged account, they can:
- Access, modify, or delete sensitive data.
- Disable security systems.
- Install malware or backdoors.
- Move laterally across the network undetected.
- Cause significant operational disruption.
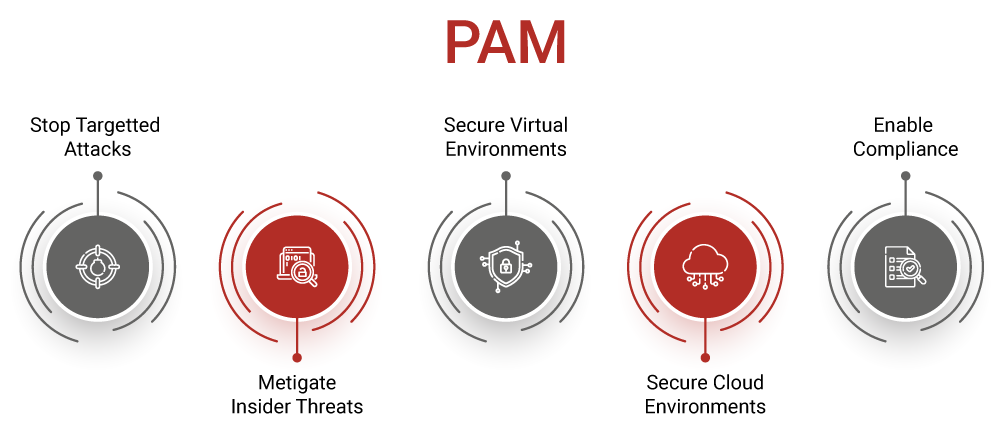
Privileged Access Management helps organizations manage and secure access to their most critical systems, applications, and data, which are typically reserved for privileged accounts. By implementing robust PAM, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface, mitigate the impact of breaches, and ensure compliance with various regulatory requirements.
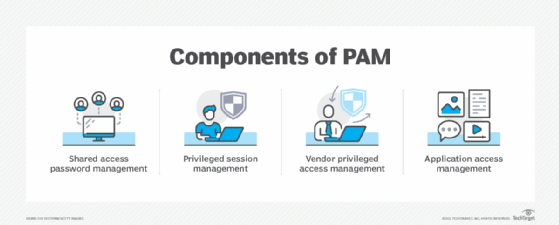
The Core Components and Strategies of PAM
Effective Privileged Access Management is built upon several key components and strategies that work in concert to establish a secure environment for privileged accounts.
Identifying and Managing Privileged Identities
The first step in any PAM strategy is to identify all privileged accounts across the entire IT ecosystem. This includes human accounts (administrators, developers, third-party vendors) and non-human accounts (applications, services, machines, scripts). Once identified, these accounts need to be managed effectively:
- Discovery and Onboarding: Automatically detect privileged accounts across diverse systems and bring them under PAM control.
- Password Vaulting: Securely store and manage privileged credentials in an encrypted vault, eliminating hardcoded passwords and reducing the risk of credential theft.
- Session Management: Provide just-in-time access, meaning privileged access is granted only when needed and for a limited duration, minimizing the window of opportunity for attackers.
- Least Privilege Principle: Grant users only the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks, thereby limiting potential damage if an account is compromised.
Monitoring and Auditing Privileged Sessions
Beyond simply controlling access, a robust Privileged Access Management solution continuously monitors and records all activities performed by privileged users. This real-time visibility is critical for detecting suspicious behavior and for forensic analysis after an incident.
- Real-time Monitoring: Observe privileged sessions as they occur, allowing security teams to intervene immediately if anomalous activity is detected.
- Session Recording: Record video and text logs of privileged sessions, providing an irrefutable audit trail for compliance, incident response, and post-incident analysis.
- Alerting and Reporting: Generate alerts for policy violations or suspicious activities, and produce detailed reports on privileged access usage for compliance and security audits.
Preventing Unauthorized Access and Cyberthreats
The ultimate goal of Privileged Access Management is to prevent unauthorized access and protect against cyberthreats. This involves a combination of proactive and reactive measures:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforce MFA for all privileged access requests, adding an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
- Threat Detection: Utilize behavioral analytics to identify deviations from normal privileged user behavior, signaling potential compromises.
- Automated Remediation: Implement automated responses to detected threats, such as terminating suspicious sessions or rotating compromised credentials.
- Secure Remote Access: Provide secure, audited pathways for remote privileged access, eliminating the need for VPNs or direct exposure of critical systems to the internet.
PAM in Action: Safeguarding Sensitive Data and Systems
The principles of Privileged Access Management are universally applicable across various industries and types of organizations, from energy providers to legal entities. The need to protect sensitive information and critical infrastructure underscores the broad relevance of PAM.
Protecting Critical Infrastructure: The Oncor Example
Organizations like Oncor Electric Delivery, which provide essential services to millions, represent critical infrastructure. The security of their systems directly impacts public safety and economic stability. More than 13 million Texas residents receive energy from Oncor through their chosen retail electric provider. Such an extensive network, managed by personnel working tirelessly (e.g., "Oncor damage assessment, vegetation management and power restoration personnel have been working since the winter storm’s arrival"), requires unparalleled security measures.
For a utility company, privileged access could include control over power grid systems, customer billing databases, and weather monitoring systems ("Leveraging the power of our weather monitoring systems, Oncor has developed Weather Current, a community outreach effort to keep you informed about potentially dangerous conditions in your area"). Unauthorized access to these systems could lead to widespread power outages, data breaches affecting millions of customers ("Sign in to access Oncor Electric Delivery services and manage your account securely," "Log in to Oncor Electric Delivery to access your account and manage your energy services securely," "Sign up to receive alerts and status updates about power outages"), or even physical harm. PAM ensures that only authorized Oncor personnel can access and manage these critical assets, and that their activities are monitored. This includes securing the processes for account management, like password resets ("After receiving the email with your reset code, enter the code in the box below and click submit reset code button"), ensuring that even routine administrative tasks are protected from compromise.
Securing High-Profile Information: Lessons from Sensitive Investigations
Beyond critical infrastructure, the protection of sensitive, high-profile information is another area where Privileged Access Management plays a vital role. Consider the handling of confidential legal documents or investigation files, such as those that might have been part of the Jeffrey Epstein investigation. "Pam Bondi sought to move past questions about her handling of the Justice Department's files from the Jeffrey Epstein investigation, as pressure continued to grow for her." This scenario highlights the immense sensitivity and public scrutiny surrounding certain types of data.
For legal firms, government agencies, or any entity handling highly confidential information, privileged access to these files must be meticulously controlled. A robust PAM system would ensure that only authorized legal teams or investigators could access, view, or modify such documents, with every action logged and audited. This prevents unauthorized leaks, tampering, or misuse of sensitive information, upholding the integrity of investigations and protecting the privacy of individuals involved. The ability to control and audit who accesses sensitive files, like those mentioned in "Bondi's announcement came after an explosive Wall Street Journal report about a letter Trump sent to Epstein in 2003," is paramount for maintaining trust and preventing compromise.
Implementing PAM: Best Practices for Organizations
Successfully deploying and maintaining a Privileged Access Management solution requires a strategic approach. Here are some best practices:
- Start Small, Scale Up: Begin by identifying the most critical systems and privileged accounts, then gradually expand the PAM scope across the organization.
- Automate Where Possible: Automate privileged credential rotation, session management, and access provisioning to reduce manual errors and enhance security.
- Integrate with Existing Security Tools: Ensure PAM integrates seamlessly with identity management, SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), and other security solutions for a unified defense.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Continuously audit privileged access policies and user activities to identify and address potential vulnerabilities or policy deviations.
- User Training: Educate privileged users on the importance of PAM and secure access practices to foster a security-aware culture.
- Define Clear Policies: Establish clear, well-documented policies for privileged access, including who can request it, for what purpose, and for how long.
By adhering to these practices, organizations can maximize the effectiveness of their Privileged Access Management investment and build a stronger defense against sophisticated cyber threats.
The E-E-A-T and YMYL Principles in PAM
In the realm of cybersecurity, particularly concerning a critical solution like Privileged Access Management, the principles of Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) are paramount. For organizations, demonstrating E-E-A-T in their cybersecurity posture, especially concerning PAM, builds confidence among stakeholders, customers, and regulators. Expertise in PAM means having deep knowledge of its technical intricacies and strategic implementation. Experience comes from successfully deploying and managing PAM solutions in real-world scenarios. Authoritativeness is established by being a recognized leader or trusted source in cybersecurity. Trustworthiness is built through consistent adherence to best practices, transparency, and a proven track record of protecting sensitive data.
Furthermore, PAM directly addresses Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) implications. Cybersecurity breaches, particularly those involving privileged access, can have catastrophic financial consequences (loss of revenue, regulatory fines, legal costs) and can severely impact an individual's or organization's "life" (reputational damage, loss of intellectual property, operational shutdowns, and even physical harm in the case of critical infrastructure). By securing privileged access, PAM directly mitigates these high-stakes risks, making it a critical component of any organization's strategy to protect its most valuable assets and ensure its very survival in the digital age.
The Future of Privileged Access Management
The landscape of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, and so too is Privileged Access Management. As organizations embrace cloud computing, DevOps, and artificial intelligence, PAM solutions are adapting to secure these new environments. The focus is shifting towards more dynamic, adaptive access controls that leverage machine learning to detect anomalies and automate responses in real-time.
The integration of PAM with broader identity and access management (IAM) frameworks will become even more seamless, creating a holistic security ecosystem. The rise of "zero trust" architectures, which assume no user or device can be trusted by default, will further elevate the importance of PAM as a foundational element for verifying and controlling every access request. Ultimately, the future of Privileged Access Management lies in its ability to provide granular, intelligent, and automated control over every privileged interaction, ensuring that organizations remain resilient against the ever-growing array of cyber threats.
Conclusion
Privileged Access Management is an indispensable shield in the modern cybersecurity arsenal. By meticulously controlling, monitoring, and protecting privileged accounts, PAM acts as a critical defense line, safeguarding an organization’s most sensitive data and critical systems from unauthorized access and cyberthreats. From preventing the exploitation of administrative credentials to securing the operational technology of essential service providers like Oncor, its importance cannot be overstated.
In an era where data breaches are not a matter of 'if' but 'when,' investing in robust Privileged Access Management is a proactive step towards building a resilient and secure digital infrastructure. It's about ensuring that the keys to your kingdom remain firmly in the right hands, under constant vigilance, thereby protecting not just your data, but your entire organizational integrity and future.
Is your organization's privileged access truly secure? Don't leave your most critical assets vulnerable.
Explore